Missions & Projects
Alphabetical
By Last Name:
Displaying records 1 to 18 of 18.
Show:
Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ)
ASIA-AQ is an opportunity for international collaboration, working with local partners to apply multi-perspective observations in a consistent strategy across interested Asian countries to improve both specific understanding of local air quality issues and general understanding of common challenges in the interpretation of satellite observations and modeling of air quality.

Arctic- Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE)
Climate change in the Arctic and Boreal region is unfolding faster than anywhere else on Earth, resulting in reduced Arctic sea ice, thawing of permafrost soils, decomposition of long- frozen organic matter, widespread changes to lakes, rivers, coastlines, and alterations of ecosystem structure and function. NASA's Terrestrial Ecology Program is conducting a major field campaign, the Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE), in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. ABoVE seeks a better understanding of the vulnerability and resilience of ecosystems and society to this changing environment.

Blueflux
BlueFlux is supported by the NASA Carbon Monitoring System to measure fluxes of carbon dioxide and methane emissions over blue carbon ecosystems. The measurements are made using chambers, flux towers and aircraft flux instruments, including the CARbon Flux Experiment (CARAFE) payload. The data products will be used by local stakeholders to support mangrove and sawgrass restoration for carbon sequestration.
Key Staff
- Principal Investigator: BENJAMIN POULTER
- Co Investigator: Lola Fatoyinbo
- Co Investigator: Glenn Wolfe

GEOS-5 Nature Run, Ganymed Release (7km-G5NR)
The GEOS-5 Nature Run (Ganymed Release) is a 2-year global, non-hydrostatic mesoscale simulation for the period June 2005 through May 2007 with a 7 km horizontal resolution. In addition to standard meteorological parameters (wind, temperature, moisture, surface pressure), this simulation includes 15 aerosol tracers (dust, seasalt, sulfate, black and organic carbon), O3, CO and CO2.
This model simulation is driven by prescribed sea-surface temperature and sea-ice, daily volcanic and biomass burning emissions, as well as high-resolution inventories of anthropogenic sources.
sm.jpg)
GMAO Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSE)
A project to develop, validate, and apply a capability using GEOS-5 for conducting observing system simulation experiments.
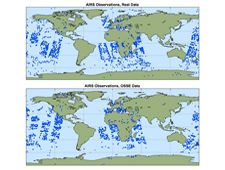
Land, Atmosphere Near real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE)
NASA's Land, Atmosphere Near real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE) provides access to near real-time (NRT) data and imagery generated from processing select instrument data (e.g. MODIS, VIIRS, OMI, OMPS, AIRS, MLS, etc,) meeting the timely needs of users interested in monitoring a wide variety of natural and man-made phenomena.

Miniaturized Laser Heterodyne Radiometer (mini-LHR)
A portable ground instrument for measuring CO2 and CH4 in the Earth's atmospheric column.
Key Staff
- Principal Investigator: Emily Wilson
- Project Scientist: Graham Allan
- Project Scientist: Hilary Melroy
- Project Scientist: Lesley Ott
- Project Scientist: Gregory Clarke
- Project Scientist: Matthew Mclinden

Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)
MODIS (or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) is a key instrument aboard the Terra (originally known as EOS AM-1) and Aqua (originally known as EOS PM-1) satellites. Terra's orbit around the Earth is timed so that it passes from north to south across the equator in the morning, while Aqua passes south to north over the equator in the afternoon. Terra MODIS and Aqua MODIS are viewing the entire Earth's surface every 1 to 2 days, acquiring data in 36 spectral bands, or groups of wavelengths (see MODIS Technical Specifications). These data will improve our understanding of global dynamics and processes occurring on the land, in the oceans, and in the lower atmosphere. MODIS is playing a vital role in the development of validated, global, interactive Earth system models able to predict global change accurately enough to assist policy makers in making sound decisions concerning the protection of our environment.

Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2)
The Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2) provides data beginning in 1980 and runs a few weeks behind real time. Alongside the meteorological data assimilation using a modern satellite database, MERRA-2 includes an interactive analysis of aerosols that feed back into the circulation, uses NASA's observations of stratospheric ozone and temperature (when available), and takes steps towards representing cryogenic processes.

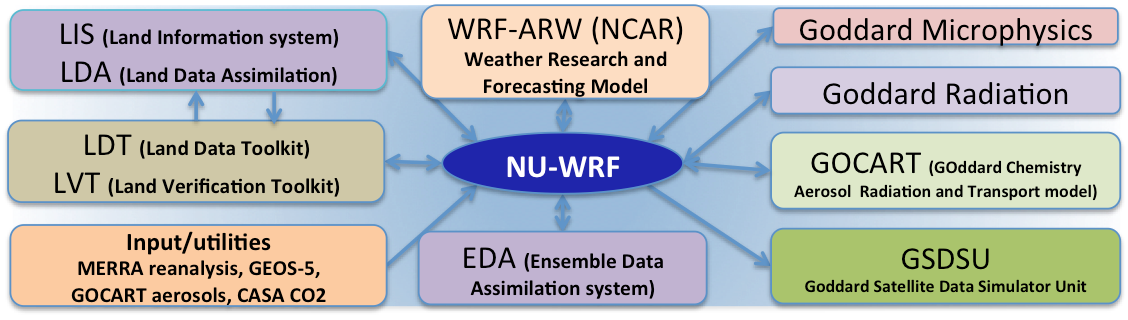
NASA-Unified Weather Research and Forecasting (NU-WRF)
The NASA-Unified Weather Research and Forecasting (NU-WRF) model is an observation-driven regional earth system modeling and assimilation system at satellite-resolvable scale. NU-WRF is one of three major earth system modeling systems funded by NASA’s Modeling Analysis and Prediction (MAP) program.
National Climate Assessment support (NCA)
The GMAO interacts with the NCA providing both data and expertise in the utilization of observational analyses and retrospective analyses, and also take feedback on the development of metrics and variables important to decision-making.
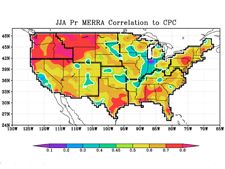
North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS)
The goal of the North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS) is to construct quality-controlled, and spatially and temporally consistent, land-surface model (LSM) datasets from the best available observations and model output to support modeling activities.

Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)
Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) is NASA’s first dedicated Earth remote sensing satellite to study atmospheric carbon dioxide from space. OCO-2 will be collecting space-based global measurements of atmospheric CO2 with the precision, resolution, and coverage needed to characterize sources and sinks on regional scales. OCO-2 will also be able to quantify CO2 variability over the seasonal cycles year after year.

PACE Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment (PACE-PAX)
PACE-PAX is a field campaign to support validation of PACE data products following launch. Validation requires a strategy of varied and extensive measurements, as discussed in the PACE Science Data Product Validation Plan. PACE-PAX is one component of the PACE validation plan, specifically addressing validation of new data products. Because these products are often the result of multi-parameter retrieval algorithms, focused and extensive measurements will be made as part of a dedicated field campaign. This campaign will use a robust suite of instruments deployed on aircraft, which will fly in coordination with ground and ocean-based observations and the PACE satellite overpass. It will be conducted roughly six months following the launch of PACE.
Key Staff
- Principal Investigator: Kirk Knobelspiesse
- Deputy Project Scientist: Ivona Cetinic

Soil Moisture Active-Passive Mission (SMAP)
The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission is an orbiting observatory that measures the amount of water in the surface soil everywhere on Earth. It was launched in January 2015 and started operation in April 2015. The SMAP radiometer has been operating flawlessly. The radar instrument, ceasing operation in early 2015 due to failure of radar power supply, collected close to 3 months of science data. The prime mission phase of three years was completed in 2018, and since then SMAP has been in extended operation phase.
Key Staff
- Science Team Member: Rolf Reichle
- Calibration Team Member: Emmanuel Dinnat
- Deputy Project Scientist: Rajat Bindlish
Student Airborne Research Program (SARP)
The Student Airborne Research Program (SARP) is an eight-week summer internship program for rising senior undergraduate students to acquire hands-on research experience in all aspects of a scientific campaign using one or more NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories (aircraft used for SARP have included the DC-8, P-3B, C-23, UC-12B, and ER-2).

Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS)
The Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) mission will provide rapid-refresh microwave measurements over the tropics that can be used to observe the thermodynamics of the troposphere and precipitation structure for storm systems at the mesoscale and synoptic scale over the entire storm lifecycle. TROPICS comprises a constellation of CubeSats in three low-Earth orbital planes.
Westcoast & Heartland Hyperspectral Microwave Sensor Intensive Experiment (WH2yMSIE )
WHyMSIE (Westcoast & Heartland Hyperspectral Microwave Sensor Intensive Experiment) is the very first step forward towards an integrated, intelligent, and affordable PBL (Planetary Boundary Level) observing system of systems. It will bring together multiple observing nodes – i.e., space, suborbital, and ground – from passive and active sensors to enable a comprehensive and coherent picture of essential PBL thermodynamic variables such as temperature, water vapor, height, and hydrometeors to provide new understanding of the PBL that is not possible with any single sensor, observational approach, or scale.

